The Technical Education and Skills Development Authority (TESDA) is a government agency in the Philippines, established under Republic Act No. 7796 in 1994. It was established to manage and supervise technical education and skills development so Filipinos can get quality vocational training to enhance their employability and support national economic growth.
TESDA also helps by offering financial aids and cash assistance programs via scholarships to students pursuing technical-vocational education to empower individuals from various backgrounds, allowing them to acquire essential skills that meets the demands of the evolving job market.
What is TESDA?
TESDA is the abbreviated name of the Technical Education and Skills Development Authority. It is the government agency responsible for managing and supervising technical education and skills development (TESD) in the country.
It was created in an effort to unify the efforts of various government bodies involved in technical-vocational education and training (TVET), ensuring a more coordinated and efficient approach to skills development in the nation.
History

TESDA was established through Republic Act No. 7796, also known as the Technical Education and Skills Development Act of 1994. It was signed into law on August 25, 1994, as a response to the recommendations of the 1991 Congressional Commission on Education, which highlighted the need for a comprehensive and unified approach to skills development in the country. TESDA is the result of the merger of three key agencies, including:
- the National Manpower and Youth Council (NMYC) of the Department of Labor and Employment (DOLE),
- the Bureau of Technical and Vocational Education (BTVE) of the Department of Education (DepEd), formerly the Department of Education, Culture and Sports (DECS), and
- the Apprenticeship Program of the Bureau of Local Employment (BLE) of the DOLE.
Logo

The TESDA logo features important symbols that represent the agency’s mission and goals in technical education and skills development.
- Cogwheel: The outer circle of the logo looks like a cogwheel, symbolizing industry and TESDA’s focus on technical-vocational education that supports economic growth.
- Human Figure: In the center, a stylized human figure with outstretched arms forms the letter “Y,” representing TESDA’s commitment to empowering individuals through education and skills training.
- Blue Color: The blue color signifies trust and professionalism, reflecting TESDA’s dedication to providing high-quality education and services for the Filipino workforce.
- Text Around the Cogwheel: The logo encircles the full name “Technical Education and Skills Development Authority” and the year “1994,” marking TESDA’s establishment and its long-standing role in education.
Mission
TESDA’s mission explicitly states the following goal:
“TESDA sets direction, promulgates relevant standards, and implements programs geared towards a quality-assured and inclusive technical education and skills development and certification system.”
Vision
TESDA, as an institution, envisions itself as:
“The transformational leader in the technical education and skills development of the Filipino workforce.”
Core Values
TESDA’s operation is guided by the following values statement:
“We believe in demonstrated competence, institutional integrity, personal commitment, culture of innovativeness and a deep sense of nationalism.”
Quality Policy
According to its quality policy, TESDA gauges its success by how satisfied the customers are and the process by which they serve is guided by the following:
- Strategic Decisions: Making informed choices to enhance our services.
- Effectiveness: Ensuring our programs deliver desired results.
- Responsiveness: Being quick to address the needs of our customers.
- Value-Added Performance: Providing services that exceed expectations.
- Integrity: Upholding honesty and transparency in all our actions.
- Citizen Focus: Prioritizing the needs of the people we serve.
- Efficiency: Using resources wisely to maximize outcomes.
Mandate
The TESDA is mandated by law to manage and oversee the TESD system and enhance the country’s human resources through education and skills training. Its mandate includes:
- Create and carry out plans for technical education and skills development.
- Establish rules and procedures for TESD programs.
- Ensure everyone can access TESD programs across the country.
- Oversee the evaluation and certification of skilled workers.
- Assess how well TESD programs are working.
- Work with industry, labor, local governments, and training institutions to improve the TESD system.
- Integrate efforts from different sectors to ensure TESD programs support national development objectives.
Powers and Functions
TESDA is granted the following powers to create and implement coordinated technical education and skills development policies, plans, and programs:
- Create policies, plans, and guidelines after consulting with industry groups and stakeholders.
- Form committees and working groups to coordinate and monitor technical education and skills development programs at all levels.
- Enter into domestic and foreign contracts as allowed by law.
- Upgrade, merge, or phase out institutions and programs for middle-level manpower development based on user needs.
- Establish and approve trade skills standards and tests set by private industries.
- Create and manage an accreditation system for public and private institutions.
- Develop and support training programs for trainers.
- Promote the use of the dual training system as per Republic Act No. 7686.
- Collect reasonable fees for tests and training, retaining earnings for its use as per guidelines.
- Distribute resources based on recommendations for projects in the National Technical Education and Skills Development Plan.
- Determine funding schemes, such as the Levy and Grant scheme, for technical education and skills development.
- Form an Advisory Committee for expert advice, funded from the Board’s budget if necessary.
- Carry out additional duties to fulfill the purposes of TESDA as outlined in this Act.
Organizational Structure
The organizational structure of TESDA is hierarchical, with the TESDA Board at the top, setting policies and directions, and various Deputy Director Generals overseeing specific functions. Each office and division under these leaders has specialized roles that contribute to the overall mission of TESDA. This structure allows TESDA to function effectively across national, regional, and local levels, ensuring that its services reach a broad audience and meet the diverse needs of the Filipino workforce.
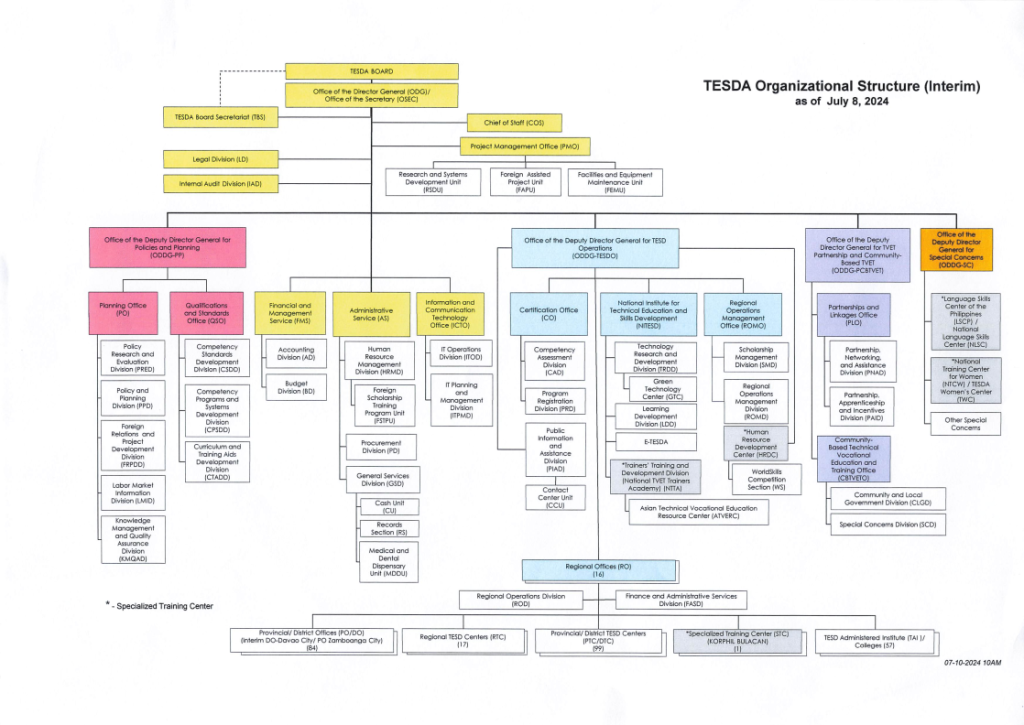
The different divisions on the TESDA organizational structure are as follows:
TESDA Board and Executive Offices
- TESDA Board: The highest decision-making body in TESDA, responsible for setting policies and strategic directions.
- Office of the Director General (ODG): Oversees the entire TESDA operation and is supported by the Office of the Secretary (OSEC) and the Chief of Staff (COS). The Project Management Office (PMO) also falls under the ODG, handling special projects and initiatives.
Deputy Director Generals
- Deputy Director General for Policies and Planning (DDG-PP): This office is responsible for developing and planning TESDA’s policies and strategies. It oversees the Planning Office (PO) and the Qualifications and Standards Office (QSO).
- Planning Office (PO)
- Qualifications and Standards Office (QSO)
- Deputy Director General for TESD Operations (DDG-TESDO): Manages the implementation of TESDA programs and services. Key offices include:
- Certification Office (CO)
- National Institute for Technical Education and Skills Development (NITESD)
- Regional Operations Management Office (ROMO)
- Deputy Director General for Partnership and Linkages (DDG-PL): Focuses on building partnerships with various stakeholders. The office is divided into:
- Partnerships and Linkages Office (PLO)
- Community-Based Technical Vocational Education and Training Office (CBTVEDO)
- Deputy Director General for Special Concerns (DDG-SC): This office addresses special areas such as the training needs of marginalized sectors. It oversees the Language Skills Center and other specialized training centers.
Supporting Divisions and Services
- Financial and Management Service (FMS): Manages TESDA’s financial resources, budgeting, and accounting.
- Administrative Service (AS): Provides administrative support, including HR management, procurement, and general services.
- Information and Communication Technology Office (ICTO): Handles IT operations, planning, and management, crucial for TESDA’s digital initiatives.
Regional and Specialized Offices
- Regional Operations Division (ROD): Supervises the regional TESDA offices, ensuring that programs and services are delivered effectively across the country.
- Specialized Training Centers: These centers focus on specific training needs, such as language skills and industry-specific skills.
Benefits
The establishment of TESDA offers several key benefits that enhance technical education and skills development.
- Improved Workforce Skills: TESDA boosts the skills of Filipino workers, increasing their competitiveness in the job market.
- Access to Education: It ensures more Filipinos can access technical education and training programs.
- Standardized Training: TESDA sets competency standards and training regulations to maintain quality across programs.
- Assessment and Certification: The authority provides assessments and certifications to validate workers’ skills and enhance employability.
- Industry Collaboration: TESDA partners with industries and local governments to align training with job market needs.
- Lifelong Learning Opportunities: It encourages continuous skill upgrading to help individuals adapt to changing job demands.
- Support for Economic Growth: By developing a skilled workforce, TESDA contributes to the country’s economic development.
- Focus on Priority Sectors: TESDA targets key sectors to create jobs and support critical industries.
- Inclusivity and Accessibility: The programs aim to provide training opportunities for marginalized groups.
- Adaptation to Global Trends: TESDA prepares the workforce for emerging industries and technologies, ensuring competitiveness in the global economy.
Coverage
TESDA offers a diverse set of programs and services that cater to a wide range of beneficiaries so they can collectively contribute to the development of a skilled workforce and support the economic growth and needs of various sectors:
- Students: Individuals seeking technical education through various training modalities, including school-based and community-based programs.
- Workers: Middle-level skilled workers aiming to enhance their skills and gain certification to improve employability.
- Unemployed Individuals: Those looking for training opportunities to increase their chances of finding jobs in priority sectors.
- Marginalized Groups: People from disadvantaged backgrounds, including those facing poverty or geographical isolation, who gain access to skills development.
- Industry Stakeholders: Employers and industry groups that benefit from a skilled workforce aligned with labor market needs.
- Local Government Units (LGUs): Collaborating with TESDA to implement training programs that address local employment issues.
- Technical Vocational Institutions (TVIs): Schools and training centers that receive accreditation and support to deliver quality technical education programs.
- Community Members: Individuals in communities participating in enterprise-based and community-based training initiatives.
- Advisory Committees: Experts from academia and industry who provide guidance on training standards and program development.
- Employers: Businesses that benefit from a more skilled and competent workforce, enhancing productivity and competitiveness.
Programs and Services
TESDA’ programs and services offered for the benefits of the groups listed above include:
1. TVET Programs
TESDA offers four training modalities – school-based, center-based, enterprise-based, and community-based – to provide equitable access to technical education and skills development programs.
2. Competency Standards Development
TESDA develops competency standards for middle-level skilled workers in the form of units of competency packaged into qualifications corresponding to critical jobs and occupations in priority industry sectors.
3. Assessment and Certification
TESDA pursues the assessment and certification of middle-level skilled workers through the Philippine TVET Competency Assessment and Certification System (PTCACS) to ensure their productivity, quality, and global competitiveness.
4. Program Registration and Accreditation
TESDA’s Unified TVET Program Registration and Accreditation System (UTPRAS) ensures compliance of Technical Vocational Institutions (TVIs) with minimum requirements before issuing government authority to offer technical vocational education programs.
5. National Technical Education and Skills Development Plan (NTESDP)
TESDA formulates a comprehensive development plan for the middle-level workforce, anchored on the vision of a globally recognized Philippine TVET as a catalyst for education, lifelong learning, workforce, and socio-economic transformation.
6. Training Regulations
TESDA promulgates Training Regulations (TR) that serve as the basis for competency-based curriculum, instructional materials, competency assessment tools, and recognition of qualifications.
7. Competency Standards
TESDA develops competency standards for middle-level skilled workers, which are the foundation for training regulations, assessment, and certification.
Video: What is TESDA
Watch this video from Philippine Education Stories and News to learn more about what TESDA is and why it is good even if the courses are mostly short-term:
Summary
TESDA is, indeed, a pillar of technical education and skills development in the country. It empowers Filipinos to acquire the skills needed for gainful employment and career advancement and provides cash assistance through scholarship programs to support its commitment to uplift the lives of Filipinos, particularly those from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Contact Information
For more information about TESDA’s programs and services, you can visit their official website or contact their main office:
Technical Education and Skills Development Authority (TESDA)
Main Office Address: East Service Road SLEX, Taguig City, Metro Manila Philippines
Contact Number: (02) 8887-7777, 0917-479-4370 (text only)
Email Address: contactcenter@tesda.gov.ph
Official Website: https://www.tesda.gov.ph/
Official Social Media Pages
Facebook: https://web.facebook.com/TESDAOfficial
Youtube: https://youtube.com/@tesdaofficial?si=3RAQnMsDlaWJAWf5
