The Department of Education (DepEd) is the Philippine government’s primary agency responsible for ensuring access to quality basic education for all Filipinos. It oversees the entire public education system, from elementary to high school, including alternative learning systems. DepEd formulates and implements policies, programs, and projects aimed at improving educational outcomes and fostering a learner-centered environment.
DepEd addresses the problem of educational inequality by providing accessible education to children across the country, regardless of socio-economic status. It can be said to shape the nation’s future, as education is key to breaking the cycle of poverty and empowering citizens. Understanding DepEd’s functions and initiatives is necessary if we are to recognize its impact on individual lives and the country’s overall development.
What is DepEd?
DepEd stands for the Department of Education, the executive agency of the Philippine government responsible for managing and regulating the country’s basic education system. Established through Republic Act 9155, also known as the Governance of Basic Education Act of 2001, DepEd’s mandate includes overseeing all public and private elementary and secondary schools, as well as alternative learning systems. The agency’s primary mission guarantees that every Filipino child has access to quality, equitable, and culture-based education.
DepEd helps develop the nation’s future by creating and implementing policies, curricula, and programs designed to produce well-rounded, competent, and patriotic citizens. It also addresses the educational needs of millions of Filipino students, providing not just academic instruction but also valuable education that aligns with national goals. But DepEd’s role isn’t confined solely to education; it also serves to improve the lives of Filipinos by offering various cash assistance programs, particularly for students and their families. The agency also helps promote social equity and foster national development, making it an integral part of the country’s progress.
History

Education in the Philippines has undergone significant transformations over the centuries. Starting with informal, vocational training during pre-Spanish times, the education system has been shaped by different colonial influences, from the religion-oriented instruction of the Spanish period to the highly centralized, English-language-based system introduced by the Americans.
The DepEd as we know it today was officially established through Republic Act 9155 in 2001. This law redefined the agency’s goals and purposes, by putting emphasis on the importance of empowering school heads and local stakeholders to improve the educational outcomes of Filipino students. DepEd also now oversees the entire basic education system, which includes elementary, secondary, and even alternative learning systems (ALS).
DepEd Logo

The DepEd logo is a symbol of the Department of Education in the Philippines and it embodies the agency’s very mission and vision through the various symbolic elements in it. These elements include:
- Shield: The shield in the logo represents the Department’s harmonious partnership with other government agencies and organizations. This collaboration is essential to effectively implement DepEd’s programs, projects, and activities aimed at improving the quality of basic education in the country.
- Philippine Map: The map of the Philippines symbolizes the nationwide scope of DepEd’s authority and responsibility in providing and governing quality basic education across the archipelago. It signifies the agency’s commitment to reach every Filipino child, no matter where they are in the country.
- Torch with Rays: The torch, radiating rays, signifies the burning desire for learning and good governance. It represents DepEd’s dedication to fostering a love for knowledge and instilling values that contribute to the holistic development of students.
- Crest with Torse: The crest with a torse at the top of the shield symbolizes DepEd as an institution that nurtures the quest for knowledge. It reflects the Department’s role in instilling values, leadership, collaboration, and excellence in every Filipino learner through education.
The logo also uses the official colors of the Philippine flag—Blue, Yellow, and Red—each symbolizing aspects of the Filipino identity and national pride, aligning with DepEd’s vision of fostering a love for the country and its heritage.
DepEd Mission
To protect and promote the right of every Filipino to quality, equitable, culture-based, and complete basic education where:
- Students learn in a child-friendly, gender-sensitive, safe, and motivating environment.
- Teachers facilitate learning and constantly nurture every learner.
- Administrators and staff, as stewards of the institution, ensure an enabling and supportive environment for effective learning to happen.
- Family, community, and other stakeholders are actively engaged and share responsibility for developing life-long learners.
DepEd Vision
We dream of Filipinos who passionately love their country and whose values and competencies enable them to realize their full potential and contribute meaningfully to building the nation. As a learner-centered public institution, the Department of Education continuously improves itself to better serve its stakeholders.
Core Values
DepEd’s mission is grounded in four core values:
- Maka-Diyos (God-fearing),
- Maka-tao (humanitarian),
- Makakalikasan (nature-loving), and
- Makabansa (patriotic).
These values guide the department’s policies and programs, ensuring that students receive an education that is not only academically rigorous but also morally and socially enriching.
Quality Policy
DepEd commits to providing quality basic education that is also accessible, inclusive, and equitable for all Filipinos. Their service pledge highlights a dedication to continuous improvement in services, ensuring that all programs, projects, and activities are aligned with the highest standards of governance, transparency, and accountability. DepEd also vows to foster a culture of excellence among its employees and stakeholders, ensuring that the needs of learners are met through collaborative efforts, innovative approaches, and a steadfast commitment to lifelong learning.
Mandate
The DepEd traces its origins back to the Education Decree of 1863, evolving significantly over time to address the educational needs of the Philippines. Its current mandate, established under Republic Act 9155 or the Governance of Basic Education Act of 2001, clearly outlines its responsibilities and objectives in the realm of basic education, which shapes the general educational landscape for all Filipinos.
- Formulates, implements, and coordinates policies, plans, programs, and projects in formal and non-formal basic education.
- Supervises all elementary and secondary education institutions, including alternative learning systems, both public and private.
- Ensures the establishment and maintenance of a complete, adequate, and integrated system of basic education aligned with national development goals.
Organizational Structure
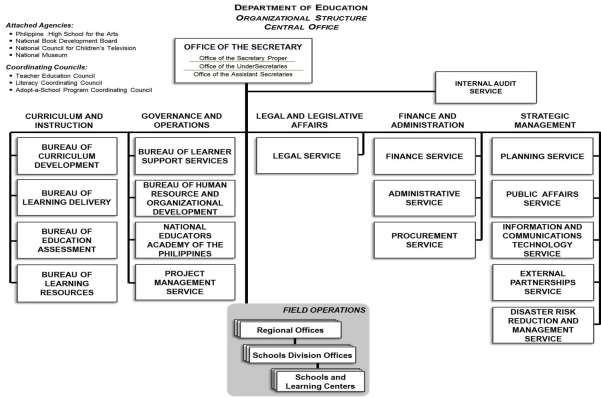
DepEd is organized into two major structural components: the Central Office and the Field Offices.
- The Central Office handles the overall administration of basic education at the national level, and
- The Field Offices manage education at the regional and local levels.
DepEd’s management structure is supported by bureaus, services, and divisions, which work together to deliver quality education across the country.
At present, DepEd operates with four (4) Undersecretaries in the following areas:
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Finance and Administration
- Governance and Operations
- Legal and Legislative Affairs
Four (4) Assistant Secretaries are also assigned in the following areas:
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Finance and Administration
- Governance and Operations
- Legal and Legislative Affairs
Supporting the Office of the Secretary (OSEC) at the Central Office are the different strands, services, bureaus, and divisions.
There are five (5) strands under OSEC:
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Finance and Administration
- Governance and Operations
- Legal and Legislative Affairs
- Strategic Management
Five (5) attached agencies:
- Early Childhood Care and Development (ECCD) Council
- National Book Development Board (NBDB)
- National Council for Children’s Television (NCCT)
- National Museum
- Philippine High School for the Arts
Three (3) coordinating councils:
- Adopt-a-School Program (ASP) Coordinating Council
- Literacy Coordinating Council (LCC)
- Teacher Education Council (TEC)
At the sub-national level, there are the following Field Offices:
- Seventeen (17) Regional Offices, plus the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM), headed by a Regional Director (or Regional Secretary in ARMM
- Two hundred twenty-one (221) Provincial and City Schools Divisions, headed by a Schools Division Superintendent
- 2,602 School Districts, headed by a District Supervisor
- 62,605 schools, broken down as follows:
- 49,209 elementary schools (38,648 public and 10,561 private)
- 13,396 secondary schools (7,976 public and 5,420 private)
Benefits
DepEd’s establishment as the primary government agency for basic education has been instrumental in promoting and ensuring access to quality education for every Filipino, along with the provision of other benefits, including the following:
1. Standardized Education System
DepEd ensures that the curriculum and educational standards across the country are consistent, providing students with a unified and quality education.
2. Wider Access to Education
By supervising both public and private institutions, DepEd makes basic education accessible to a broader population, including those in remote and underserved areas.
3. Support for Alternative Learning
DepEd offers alternative learning systems that cater to out-of-school youths and adult learners, providing them with opportunities to continue their education.
4. Curriculum Development
The agency continuously updates and improves the curriculum to make it relevant to the needs of the country, equipping students with the skills necessary for national development.
5. Teacher Training and Development
DepEd also invests in the professional development of teachers, ensuring that educators are well-trained, supported, and equipped to deliver high-quality education.
Coverage
As an agency, DepEd has a broad coverage, ensuring that education is inclusive and accessible to a wide range of beneficiaries across the country. It caters to learners of all ages and backgrounds, striving to provide quality basic education that is relevant to their needs and to the nation’s development goals. DepEd’s services extend beyond the traditional classroom setting to include various alternative learning systems and special education programs.
The beneficiaries of these programs include:
- Public and private elementary and secondary school students.
- Out-of-school youth and adult learners through alternative learning systems.
- Indigenous peoples and cultural communities with tailored educational programs.
- Students with disabilities through special education (SPED) services.
- Teachers, administrators, and education support personnel for professional development and training.
Programs, Projects, and Activities (PPA)
DepEd offers a wide range of programs and services designed to enhance the quality and accessibility of basic education in the Philippines. These initiatives include:
1. K to 12 Basic Education Program
A comprehensive curriculum that covers Kindergarten through Grade 12, designed to equip students with essential skills and knowledge for higher education, employment, and entrepreneurship.
2. Alternative Learning System (ALS)
A parallel learning system that provides a second chance to out-of-school youth and adult learners who have not completed formal basic education, offering flexible learning options and equivalency assessments.
3. Special Education (SPED)
Programs tailored for learners with special needs, ensuring they receive appropriate educational interventions and support to achieve their full potential.
4. School-Based Feeding Program
A health and nutrition initiative that provides free meals to undernourished students in public schools, including all kindergarteners and severely wasted and wasted students in grades 1–6, to improve their nutritional status and overall academic performance.
5. Brigada Eskwela
An annual nationwide volunteer program where communities, private sectors, and stakeholders collaborate to prepare public schools for the opening of classes, ensuring a conducive learning environment.
6. Dropout Reduction Program (DORP)
An intervention program to reduce high dropout rates and improve learning outcomes in public and private schools
7. Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E)
Determines if a program meets its objectives, outputs, and desired outcomes. M&E also helps identify weaknesses in a program so that adjustments can be made to get it back on track.
8. Multigrade Education Program
One of DepEd’s strategies to provide quality education to school-age children in remote communities
9. Basic Education–Learning Continuity Plan
A plan designed to ensure the safety of students, teachers, and staff, while also providing quality distance learning through self-learning modules
10. Youth Formation Division Priority Programs
- Learner Government Program: Empowers students nationwide to excel in academics, leadership, and social responsibility while fostering national pride.
- Career Guidance Program: Assists students in making informed decisions about their educational and career paths, including Senior High School track choices.
- Learner Allyship Program: Enhances inclusive participation by supporting learners with special education needs and promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion.
- Learner Formators’ and Teacher-Advisors Enhancement Programs: Provides training to educators to better manage student organizations and support students’ holistic development.
- Leadership Development Programs, Advocacies, and Campaigns: Develops students’ leadership skills and promotes positive community impact through various initiatives and special events.
- National Greening Program through the YES-O
- Campaign Against Substance Abuse through BKD
- Learners’ Convergence PH
- Special Events
Video: Byaheng 2023 ng DepEd
To learn more about DepEd, take a moment to check on the reforms and initiatives implemented by the Department of Education, led by Vice President and Secretary Sara Z. Duterte in this video by DepEd Philippines. These efforts aimed to deliver quality education and help fulfill the dreams of every Filipino child is reported as DepEd’s journey in 2023.
Summary
The DepEd is the government agency charged with shaping the country’s future through education. By making sure all Filipino children have access to accessible and affordable quality basic education, DepEd helps improve lives beyond the classroom. It also helps alleviate poverty through various cash assistance programs, creating a more equitable society where every Filipino has the opportunity to succeed.
Contact Information
For more information on DepEd and its programs and how they can benefit your family, visit the official DepEd website or contact your local DepEd office.
Department of Education (DepEd)
Main HQ address: 2nd & 5th Floor, Bonifacio Bldg, DepEd Complex, Meralco Ave, Pasig City
Contact Number: 0945 175 9777, (02) 8632-1372
Email Address: depedactioncenter@deped.gov.ph, cpu@deped.gov.ph, weprotectlearners@deped.gov.ph
Official website: https://www.deped.gov.ph/
Facebook: https://web.facebook.com/DepartmentOfEducation.PH
Youtube: https://youtube.com/@deped_ph?si=eElekuE9ob6NA6qo
